Automotive Cybersecurity by the Numbers
2021 Upstream report indicates there’s a lot of room for improvement

Cyber attacks are increasing throughout the auto industry—at factories, dealerships, fleets, customer databases and in vehicles themselves.
And the problem likely will get worse in the coming years as hackers become more savvy and the number of potential entry points rockets.
That’s the sobering news from Upstream Security’s 2021 Automotive Cybersecurity Report.
Big Picture
Here are some top-line numbers from the report, which crunched information from the media, company databases and other public sources.
207 auto-related cyber incidents worldwide have been reported in 2020 (up from 197 last year and 633 since 2010), including 106 vehicle events.
55% of the attacks this year were carried out by “black-hat” hackers with malicious or criminal intent.
(Images: Upstream)
$3.86 million cost per data breach (across all industries) in 2020, which adds up to about $600 billion per year.
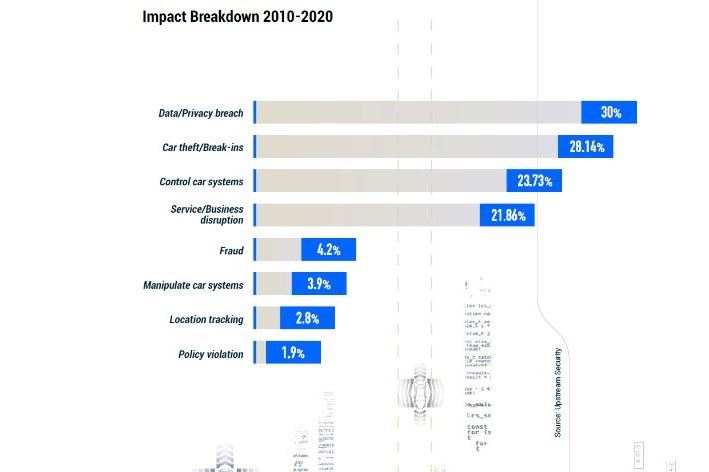
36% of this year’s automotive incidents involved data and privacy breaches versus 28% for thefts/break-ins.
300-plus vulnerabilities found in 40 ECUs developed by 10 Tier-1 companies and OEMs.
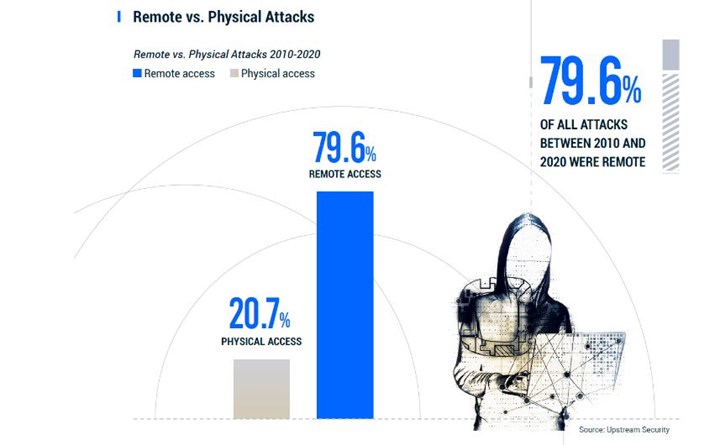
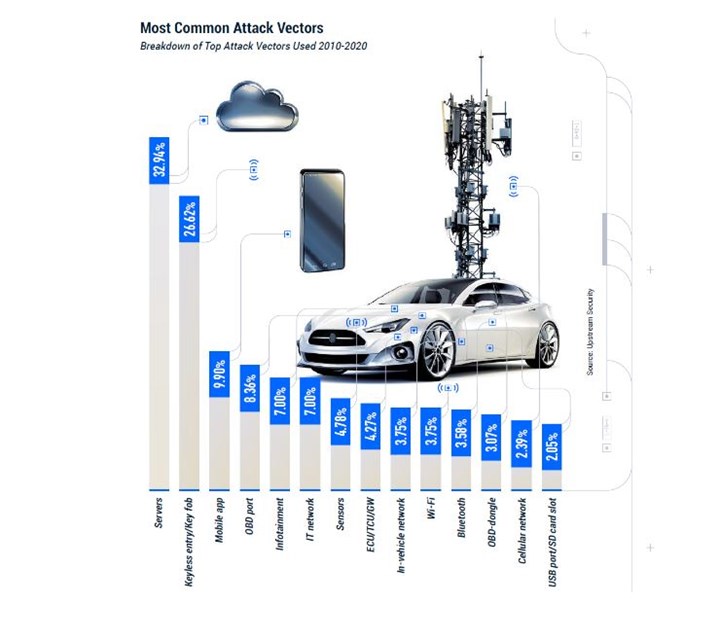
3 most common attack vectors since 2010: servers, keyless entry systems and mobile apps
78% of attacks this year were initiated remotely.
1,500 reported software vulnerabilities identified from Uber’s “bug-bounty” program, including a 13% increase this year.
4,118 vehicles were stolen in India (reported as a single event) with cheap electronic devices that enabled the thieves to unlock the vehicle, start the engine and access the vehicles' computer.
$1 million bug bounty reward offered by Tesla.
3.5 million Zoomcar users had their rental car information hacked and offered for sale on the dark web.
Steps Toward Security
It wasn’t all bad news. Carmakers and suppliers continue to introduce countermeasures to thwart hackers, while new standards (UNECE WP.29 and ISO/SAE 21434) promise more safeguards, notes Upstream, a Herzliya, Israel-based cybersecurity specialist.
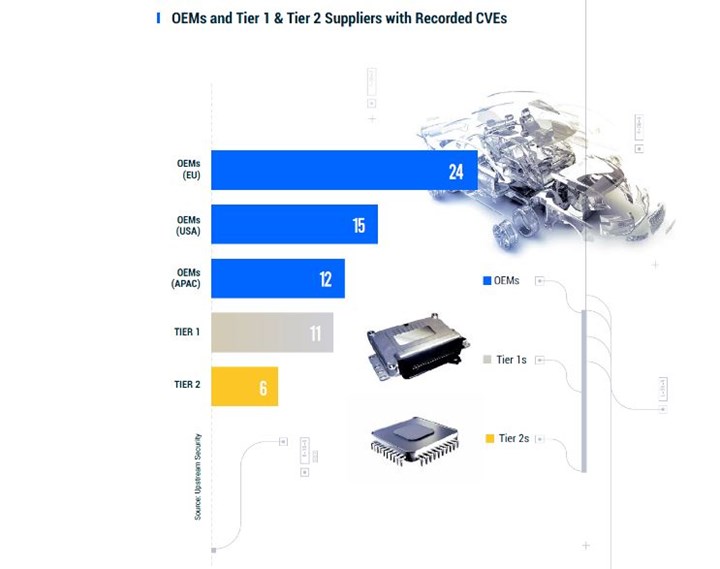
Common vulnerabilities and exposures
“We see a lot of progress has been made, especially in the last year, both by OEMs and suppliers, primarily due to the latest progress in the automotive cybersecurity standards and regulations,” attests Fay Goldstein, Upstream’s communications manager.
“To best protect themselves against future attacks, companies must take multiple approaches,” she adds, “including increasing the vehicle’s security by design, implementing multi-layered cybersecurity solutions, developing an effective VSOC (vehicle security operations center), and tracking cyber threats through automotive-specific threat intelligence.
But…
“Because of the complexities within the connected car ecosystem, and the rapid change of attack methods, there is no way for a connected vehicle to be 100% cyber secure,” Goldstein cautions. “This is a continuous cycle, a cat-and-mouse chase if you will.”
RELATED CONTENT
-
On Fuel Cells, Battery Enclosures, and Lucid Air
A skateboard for fuel cells, building a better battery enclosure, what ADAS does, a big engine for boats, the curious case of lean production, what drivers think, and why Lucid is remarkable
-
On Electric Pickups, Flying Taxis, and Auto Industry Transformation
Ford goes for vertical integration, DENSO and Honeywell take to the skies, how suppliers feel about their customers, how vehicle customers feel about shopping, and insights from a software exec
-
Choosing the Right Fasteners for Automotive
PennEngineering makes hundreds of different fasteners for the automotive industry with standard and custom products as well as automated assembly solutions. Discover how they’re used and how to select the right one. (Sponsored Content)