Hyundai Develops Wearable Robots
The Hyundai Motor Group is directing some of its attention and resources toward the development of robotic technology, which includes wearable robots, service robots and micromobility.
#robotics
The Hyundai Motor Group is directing some of its attention and resources toward the development of robotic technology, which includes wearable robots, service robots and micromobility.
The wearable robots have applicability in manufacturing operations, as shown in this photograph:
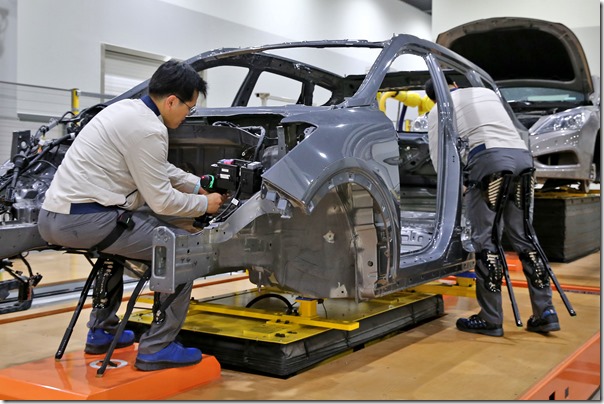

While it appears as though the person in the foreground is simply sitting on a chair, if you look to the person on the right side, you’ll see that this is actually part of what is known as the “Hyundai Chairless Exoskeleton” (H-VEX), a wearable robot.
This device weighs 1.6 kg (3.5 lb) and can support up to 150 kg (330 lb). It features waist, thigh and knee belts so it can be fitted and adjusted to the individual worker’s height. The purpose of the H-CEX is to protect the worker’s knee joints by maintaining the proper seating position.
Next up for industrial use will be the H-VEX, or the Hyundai Vest Exoskeleton. This device is engineered to reduce worker back and neck pressure when doing overhead work by providing an extra 60 kg (132 lb) of strength to the worker.
It is worth noting that Hyundai is taking these wearable robotic ideas and using them for medical applications, as well. It has the Hyundai Medical Exoskeleton (H-MEX), which can help paraplegics and elderly people with walking and negotiating staircases; this is in the process of being approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in Korea as a commercial medical device.
(Then there is the HUMA—the Hyundai Universal Medical Assist—a device that can be used to strengthen the wearer’s leg muscles when it is worn. And it also allows the wearer to run at a speed 12 km/h (7.5 mph).)
RELATED CONTENT
-
TRW Multi-Axis Acceleration Sensors Developed
Admittedly, this appears to be nothing more than a plastic molded part with an inserted bolt-shaped metal component.
-
GM Develops a New Electrical Platform
GM engineers create a better electrical architecture that can handle the ever-increasing needs of vehicle systems
-
The Koenigsegg Jesko Has An Amazing Engine
It is hard to believe that this is a vehicle in “serial” production with such extraordinary powertrain performance


.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)